Running targets in "FAKE - F# Make"
INFO
This documentation is for FAKE version 5.0 or later. The old documentation can be found here
Command line interface for the target module
If you use the Fake.Core.Target module and call Target.runOrDefault or Target.runOrList in your build script you will have the following CLI options:
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: 10: 11: 12: 13: |
|
INFO
Please refer to the general FAKE 5 runner command line interface or the Fake.Core.CommandLineParsing documentation
This means you can - for example - run fake run build.fsx --list
or fake build --list to list your targets.
To run a target MyTarget you could use fake run build.fsx -t MyTarget or fake build target MyTarget (or the other way around fake run build.fsx target MyTarget)
All parameters after -- or target <target> are given to the target as paramters. Note that this feature needs to be enabled by using Target.runOrDefaultWithArguments instead of Target.runOrDefault!
INFO
Note that the ordering of the parameters matters! This means the following are invalid (which is different to pre FAKE 5 versions):
fake run -t Target build.fs- because of ordering fake will assume-tto be the script name-
fake build -v- It will not run FAKE in verbose mode but give the parameter-vto the target parameters. This is because there is no-vin the above CLI.
Running specific targets
FAKE has a special param "target" which can be used to run specific targets in a build. We assume the following build script (build.fsx):
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: 10: 11: 12: 13: 14: 15: 16: 17: 18: 19: 20: 21: 22: 23: 24: 25: 26: 27: 28: |
|
WARNING
Previous versions of FAKE 5 used (fun () -> ...) instead of (fun _ -> ...).
We decided to change the syntax here to introduce some parameters or other features at a later point.
Using the current parameter object is not supported yet.
Now we have the following options:
fake run build.fsx -t "Build"--> starts the Build target and runs the dependency Cleanfake run build.fsx -t "Build" --single-target--> starts only the Build target and runs no dependenciesfake run build.fsx -s -t Build--> starts only the Build target and runs no dependenciesfake run build.fsx--> starts the Deploy target (and runs the dependencies Clean and Build)
Script with arguments
Example:
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: 10: 11: 12: 13: 14: 15: 16: 17: 18: 19: 20: 21: 22: 23: 24: 25: 26: 27: 28: 29: 30: 31: |
|
Everything after the target will be interpreted as argument for the target:
fake run build.fsx target MyTarget --arg-->--argwill be contained inargsfake build -t MyTarget --arg-->--argwill be contained inargs, because--argis not a valid argument for theFake.Core.Target(see command line spec above)
Targets with arguments
Example:
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: |
|
Everything after the target will be interpreted as argument for the target:
fake run build.fsx target MyTarget --arg-->--argwill be contained inp.Context.Argumentsfake build -t MyTarget --arg-->--argwill be contained inp.Context.Arguments, because --arg is not a valid argument for theFake.Core.Target(see command line spec above)
You can access the arguments from every target executed along the way.
Setting build status
You can set the build status automatically using Target.updateBuildStatus. To do this you need to use the Target.WithContext functions to run a target and retrieve the context information:
Example:
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: 10: 11: 12: 13: 14: 15: 16: 17: 18: 19: 20: 21: 22: 23: 24: 25: 26: 27: 28: 29: 30: |
|
Final targets
Final targets can be used for TearDown functionality. These targets will be executed even if the build fails but have to be activated via Target.ActivateFinal().
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: |
|
Build failure targets
Build failure targets can be used to execute tasks after a build failure.
These targets will be executed only after a build failure but have to be activated via activateBuildFailure().
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: |
|
Using FAKE's parallel option
Since multithreading is beneficial (especially for large projects) FAKE allows to specify the number of threads used for traversing the dependency tree. This option of course only affects independent targets whereas dependent targets will still be executed in order.
Setting the number of threads
The number of threads used can be set using the environment variable parallel-jobs or using the --parallel parameter.
This can be achieved in various ways where the easiest one is to use the parameter:
fake run *YourBuildScript* --parallel 8
Note that the dependency tree will be traversed as usual whenever setting parallel-jobs to a value <= 1 or omiting it entirely.
Issues
- Running targets in parallel is of course only possible when the target-functions themselves are thread-safe.
- Parallel execution may also cause races on stdout and build-logs may therefore be quite obfuscated.
- Error detection may suffer since it's not possible to determine a first error when targets are running in parallel
Due to these limitations it is recommended to use the standard sequential build whenever checking for errors (CI, etc.) However when a fast build is desired (and the project is e.g. known to build successfully) the parallel option might be helpful
Example
When using this parallel option, Fake resolves the build dependency hierarchies from the described paths and builds independend paths as parallel if you have multiple CPUs available. For example this dependency tree:
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: 10: 11: 12: 13: 14: 15: 16: |
|
...would be treated as follows:
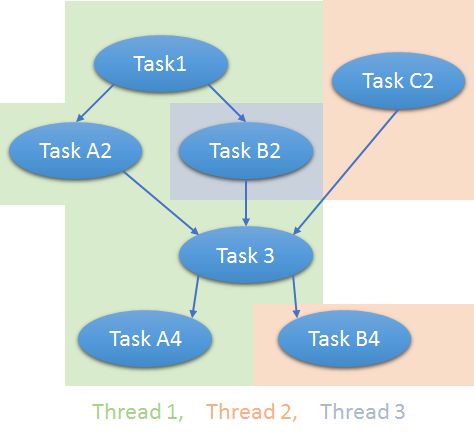
This is in addition to that that MSBuild may use multiple threads when building one solution having multiple independent project-files.
Soft dependencies
Typically you will define dependencies among your targets using the ==> and <== operators, and these
dependencies define the order in which the targets are executed during a build.
You can also define soft dependencies among targets using the ?=> and <=? operators. For example, you might
say that target B has a soft dependency on target A:
1: 2: 3: |
|
With this soft dependency, running B will not require that A be run first. However it does mean that if A is run (due to other dependencies) it must be run before B.
Example
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: 10: 11: 12: 13: 14: 15: 16: |
|
from Microsoft.FSharp.Collections